Algorithms Analyses On this page 📐 Algorithm complexity# Time complexity# Time complexity specifies how long it will take to execute an algorithm as a function of its input size. It provides an upper-bound on the running time of an algorithm.
Space complexity# Space complexity specifies the total amount of memory required to execute an algorithm as a function of the size of the input.
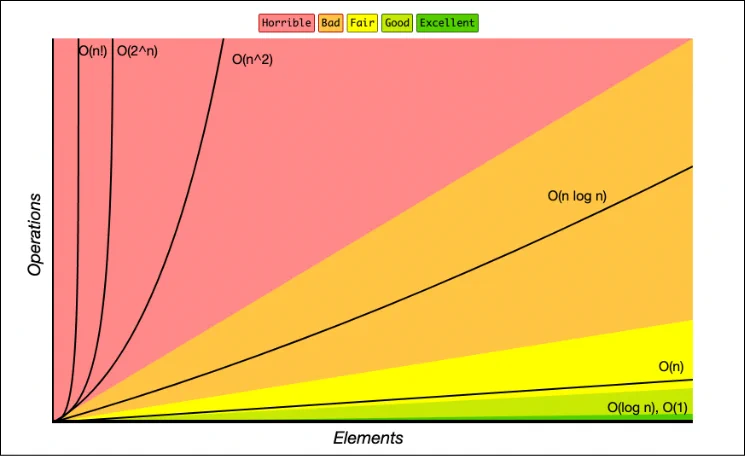
📈 Order Of Growth# Classifications# order of growth name description example 1 Constant statement add two numbers log N Logarithmic divide in half binary search N Linear loop find the maximum N log N Linearithmic divide and conquer mergesort N2 Quadratic double loop check all pairs N3 Cubic triple loop check all triples 2n Exponential exhaustive search check all subsets
Simplification# Drop constants. Constants do not affect the algorithm’s growth rate relative to its input.Lower-Order terms. There is a focus on the dominant term that contributes the most to the growth rate.Use Summation for Multiple operations. Multiple operations with a different time complexity can be summed.
O(n) and O(log n) -> O(n + log n) -> O(n) (because of the dominant term )
Drop Non-Dominant Terms in Additions. We need to leave only the terms that dominate the growth rate.Multiplication rule for Nested arrays.
O(n) loop with a nested O(m) loop -> O(n * m)
Consider the Worst-Case Scenario. Big O notation focuses on the worst-case scenarios, so it needs to be simplified based on the worst-case analysis.🔭 Asymptotic Notations# There are mathematical notations used to describe an algorithm’s performance in relation to the amount of input data:
Big O - worst case (upper-bound on cost)Big Ω (Omega) - best case (lower-bound on cost)Big Θ (Theta) - average case (“expected” cost)Big O# Big O notation represents an algorithm’s worst-case complexity. It defines how the performance of the algorithm will change as an input size grows.
Resources#